Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
The Transesophageal Echocardiogram, or TEE, is a type of echocardiogram that holds a distinctive place within the spectrum of heart imaging techniques. Unlike other echocardiograms that examine the heart from the outside, TEE takes us on an intimate journey inside the body, offering a uniquely close look at the heart’s anatomy and function. The following sections delve deeper into the TEE, exploring its scientific underpinnings, procedural steps, clinical applications, advantages, and future prospects.
The Science Behind TEE
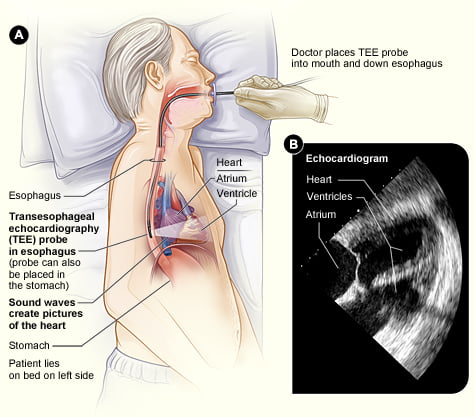
The TEE relies on the fundamental principles of ultrasound technology, much like its counterparts. However, the distinctive aspect of TEE lies in the positioning of the ultrasound transducer. In a TEE, the transducer is incorporated at the end of a flexible tube or probe. This probe is carefully guided down the patient’s esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
Why the esophagus, you might wonder? It’s because of its close proximity to the heart. This allows the TEE to generate high-resolution images of the heart structures, which might not be as visible or detailed in a conventional transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE), especially in patients with certain conditions that interfere with the ultrasound waves.
The TEE Procedure: An Inside View
The TEE is a minimally invasive procedure, requiring some preparation on the patient’s part. The patient is usually asked to fast for several hours before the test, to clear the stomach and reduce the risk of aspiration.
During the procedure, the patient’s throat is numbed with a local anesthetic, and a sedative is administered to help them relax. The TEE probe, a long, thin, flexible tube, is then gently inserted into the mouth and guided down the esophagus.
Once the probe is correctly positioned, the transducer at its end emits ultrasound waves, which bounce off the heart and return to the transducer as echoes. These echoes are transformed into detailed images of the heart, which are displayed on a monitor for the physician’s interpretation. The procedure typically takes between 30 to 60 minutes.
Clinical Applications of TEE
Due to its proximity to the heart, TEE allows for a detailed evaluation of complex heart structures such as the valves, the left atrium, and the aorta. It can detect abnormalities that might not be visible on a standard TTE, such as blood clots, valve infections, or aortic dissections.
Furthermore, TEE plays a pivotal role in guiding heart surgeries and procedures. For instance, it is often used intraoperatively during heart valve surgery to assess the valves before and after repair or replacement. It is also indispensable during procedures like catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation, where it guides the catheter to the correct heart location and monitors for possible complications.
Benefits and Limitations
TEE offers several advantages, such as high-resolution images and the ability to visualize certain heart structures more clearly than a TTE. However, it also comes with certain drawbacks. Being an invasive procedure, it requires sedation and carries a small risk of complications such as throat discomfort or minor bleeding. Furthermore, it needs to be performed by a skilled practitioner and may not be as readily available as TTE.
The Future of TEE
Looking ahead, advancements in ultrasound technology promise to enhance the capabilities of TEE. One exciting development is the advent of three-dimensional (3D) TEE, which can create detailed 3D models of heart structures, providing even more in-depth information to guide treatment decisions.
References:
- American Heart Association – Transesophageal Echocardiography
- Mayo Clinic – Transesophageal Echocardiogram
- Harvard Health – Transesophageal Echocardiogram
- Johns Hopkins Medicine – Transesophageal Echocardiogram
- Cleveland Clinic – Transesophageal Echocardiogram
My other posts: